
-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Total Solution
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
-
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp



When it comes to powering your appliances and devices during emergencies or outdoor adventures, an electric inverter is an essential investment. However, with the multitude of options available on the market today, choosing the right electric inverter can feel overwhelming. The critical factors to consider include your unique power needs, the type of devices you plan to run, and your budget. Understanding these elements not only helps you make an informed decision but also ensures that you select an inverter that meets your specific requirements.
Electric inverters come in various types and sizes, each tailored for different applications. For some, portability is a priority, making smaller, lightweight models more appealing. For others, the focus may be on power output, especially for those needing to run larger appliances. Moreover, budget constraints can play a significant role in determining which model you can afford. By evaluating your power usage, understanding different inverter technologies, and assessing your financial parameters, you can confidently navigate the selection process and find the perfect electric inverter to suit your setup.
In this guide, we will break down the key considerations involved in choosing the right electric inverter to ensure that you make a purchase that aligns with your workload and financial goals. Whether you require a reliable backup power source for home use or a compact solution for road trips, understanding how to choose wisely will lead you to the best inverter for your needs.

Electric inverters are essential devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), allowing you to power a variety of appliances and devices that require AC electricity. Understanding the basic functions of electric inverters is crucial before making a purchase. Inverters come in different sizes and power outputs, which determine how many devices you can run at once. It's important to consider whether you need a pure sine wave inverter, which is ideal for sensitive electronics, or a modified sine wave inverter, which may be suitable for simpler devices.
When selecting the right inverter for your needs and budget, consider the power requirements of the devices you plan to use. Assess the total wattage needed and choose an inverter that exceeds this requirement to avoid overloading. Remember to factor in peak power ratings, as some devices require additional power when starting up.
**Tips:** Always read the specifications carefully and consult with professionals if you're unsure about the wattage requirements. Additionally, consider the inverter's efficiency rating, as a higher efficiency can lead to lower energy costs in the long run. Lastly, think about battery compatibility; some inverters are designed to work specifically with certain battery types, which can impact your overall performance and charging capabilities.
| Inverter Type | Power Output (W) | Input Voltage (V) | Efficiency (%) | Price ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Sine Wave | 1500 | 12 | 85 | 150 |
| Pure Sine Wave | 2000 | 24 | 90 | 300 |
| Grid Tie | 3500 | 48 | 95 | 800 |
| Off Grid | 5000 | 48 | 92 | 1200 |
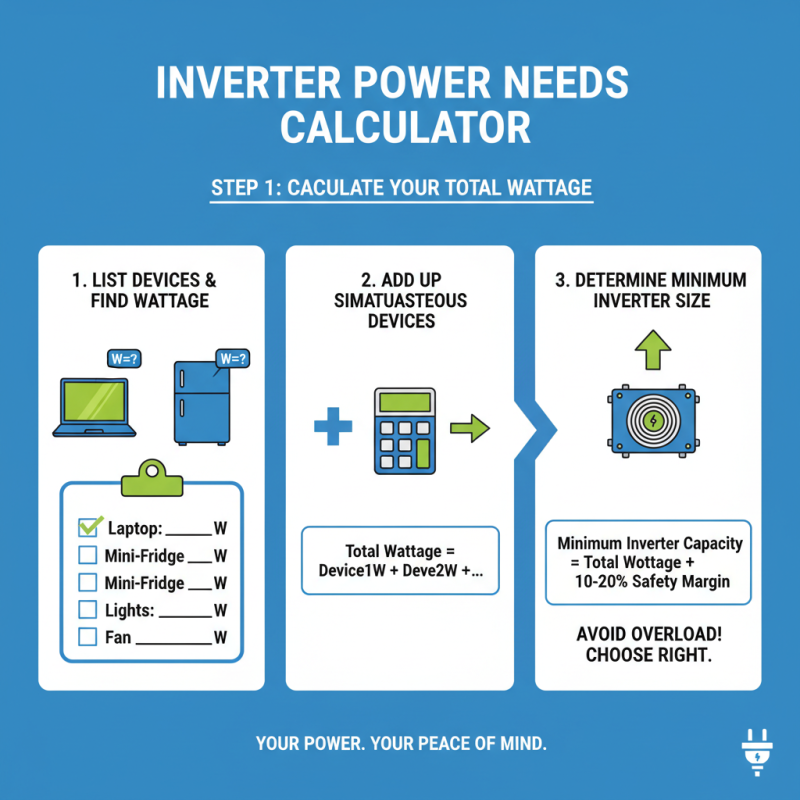
When selecting an electric inverter, the first essential step is to identify your power needs, which begins by calculating wattage and load requirements. To do this, start by listing all the devices you plan to connect to the inverter. Each device will have a specified wattage rating, usually found on a label or in the user manual. Add up the wattage for all devices you intend to run simultaneously. This total will give you a baseline for the minimum inverter capacity you'll need to meet your energy demands without overloading the system.
It’s also important to consider the startup or surge wattage of devices, as many appliances require more power to start than they do to run. For instance, motors in refrigerators and air conditioners may call for several times their running wattage during start-up. To ensure that the inverter can handle this initial surge, factor in the increased wattage when calculating your total needs. By accurately assessing both running and startup wattage, you can choose an inverter that not only meets your current requirements but also allows for future appliances or expanded use without concern.
When choosing the right electric inverter for specific applications, it's essential to evaluate the various types available in the market. Inverters generally fall into three categories: pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave. Pure sine wave inverters are ideal for sensitive electronics, such as medical equipment and high-end audio systems, as they produce clean and stable electricity. Reports indicate that nearly 30% of residential solar power users opt for pure sine wave inverters due to their reliability and efficiency in delivering consistent power.
Modified sine wave inverters, while more affordable, might not be suitable for all devices, particularly those with sophisticated microprocessors. They are typically used in applications such as powering basic appliances and tools. A market survey revealed that over 50% of small businesses employ modified sine wave inverters for their energy needs, recognizing a balance between cost-efficiency and performance for less sensitive devices.
Tip: Always assess the wattage requirements of your applications. An inverter should be able to handle the total wattage of all devices you plan to use. Additionally, consider the surge wattage, which is the extra power that certain devices draw when they first start. This goes a long way in ensuring you select an inverter that meets your specific needs without the risk of overload.
When selecting an electric inverter, the first step is to establish a clear budget that reflects both your financial limits and your essential needs. Determine how much you can spend without compromising your overall financial security. Inverters come with a wide range of prices, influenced by factors such as power capacity, efficiency ratings, and additional features. It's essential to assess the specific requirements of the devices you plan to power, as this will significantly influence the type and size of inverter you need.
Once you have a budget in mind, it's important to balance cost and features to make an informed decision. Consider whether you need advanced features like remote monitoring, automatic shutdown, or pure sine wave output, or if a basic model will suffice for your needs. Make a list of the features that are most crucial for your intended use and compare different models in your price range. Don’t be swayed by flashy extras that may not add significant value to your setup; instead, focus on features that enhance performance and reliability while staying within your budget. By prioritizing essential functionality over unnecessary luxuries, you can find an inverter that meets both your needs and your financial constraints.

When selecting an electric inverter, it’s essential to consider additional features that can enhance its performance and usability. One important aspect is the inverter’s wattage rating, which determines how much power it can handle. Look for inverters with a capacity that exceeds your maximum power requirement, allowing for potential future expansions. Moreover, understanding the inverter's efficiency rating is crucial, as higher efficiency means less energy loss during the conversion process, ultimately saving on electricity bills.
Another key feature to evaluate is the inverter's waveform output. Pure sine wave inverters are ideal for sensitive electronic devices, as they provide cleaner power and reduce the risk of damage. Additionally, consider inverters with built-in safety features, such as overload protection, short-circuit protection, and thermal shutdown capabilities, which ensure reliability and safety during operation. Finally, portability can be a vital feature if you plan to use the inverter for outdoor activities or in various locations. Look for lightweight models with convenient handles or carrying cases to make transportation easier.





